Cast Iron Welding (svařování litiny): Essential Insights for Your Repair Projects

Cast iron has been a staple in manufacturing and everyday items for centuries, prized for its durability, heat retention, and affordability. From engine blocks and cookware to machinery parts and antique furniture, cast iron components are everywhere. However, when these items crack or break, repairing them through welding can be a daunting task. Unlike welding steel or aluminum, cast iron presents unique challenges due to its high carbon content, which makes it prone to cracking and brittleness during the welding process. In this blog, we'll dive into the intricacies of cast iron welding, offering practical advice to help you understand when and why to seek professional help for your welding needs.
Why Cast Iron Welding Is Challenging
Cast iron's composition—typically containing 2-4% carbon—creates a material that's hard and wear-resistant but also brittle. When heated during welding, the carbon can form hard, brittle structures like martensite in the heat-affected zone (HAZ), leading to cracks if not managed properly. Common issues include:
- Thermal Stress: Rapid heating and cooling cause expansion and contraction, resulting in fractures.
- Porosity and Impurities: Cast iron often has embedded dirt, oil, or graphite flakes that can contaminate the weld.
- Pre-Existing Cracks: Invisible micro-cracks in old castings can propagate during welding.
These challenges make DIY attempts risky, often leading to further damage or weakened repairs. Professional welders, equipped with specialized tools and experience, can mitigate these risks effectively.
Key Techniques for Welding Cast Iron
There are several proven methods to weld cast iron successfully, each suited to different scenarios. The choice depends on the part's size, the extent of damage, and the required strength of the repair.
1. Preheating (Hot Welding)
This is one of the most reliable methods for achieving strong, crack-free welds. By slowly heating the entire piece to 500-1200°F (260-650°C) before welding, you reduce thermal shock. Use nickel-based electrodes (like ENi-CI) for their compatibility with cast iron's expansion properties. After welding, allow slow cooling in an insulated environment to prevent cracking.
2. Cold Welding
For situations where preheating isn't feasible—such as large or fixed installations—cold welding uses specialized rods without high heat. Techniques like stick welding with low-heat input and peening (hammering the weld bead while hot) help relieve stress. This method is quicker but may not be as durable for high-stress applications.
3. Brazing
Not true welding, but an effective alternative where fusion isn't required. Using a brass or bronze filler at lower temperatures (around 1500°F or 815°C) creates a strong bond without melting the base metal. Ideal for decorative or low-load repairs, like antique cast iron pieces.
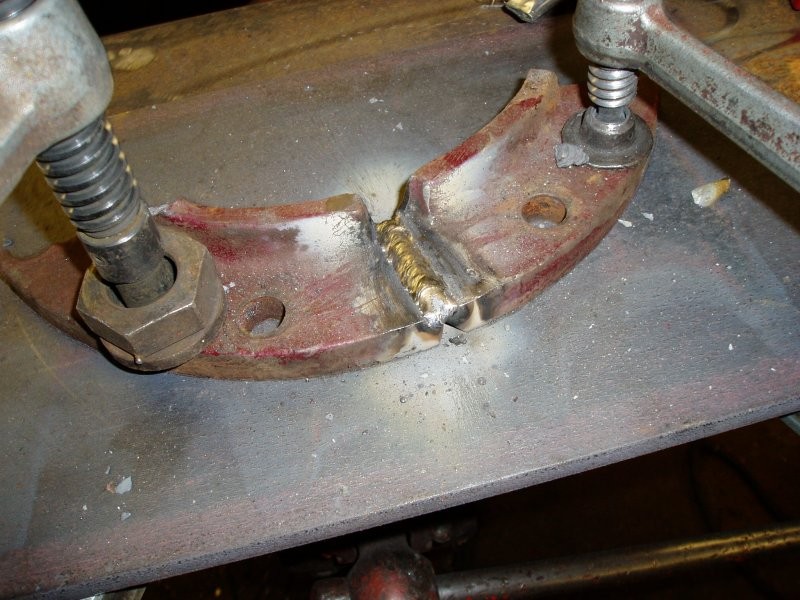
Step-by-Step Preparation for Successful Welds
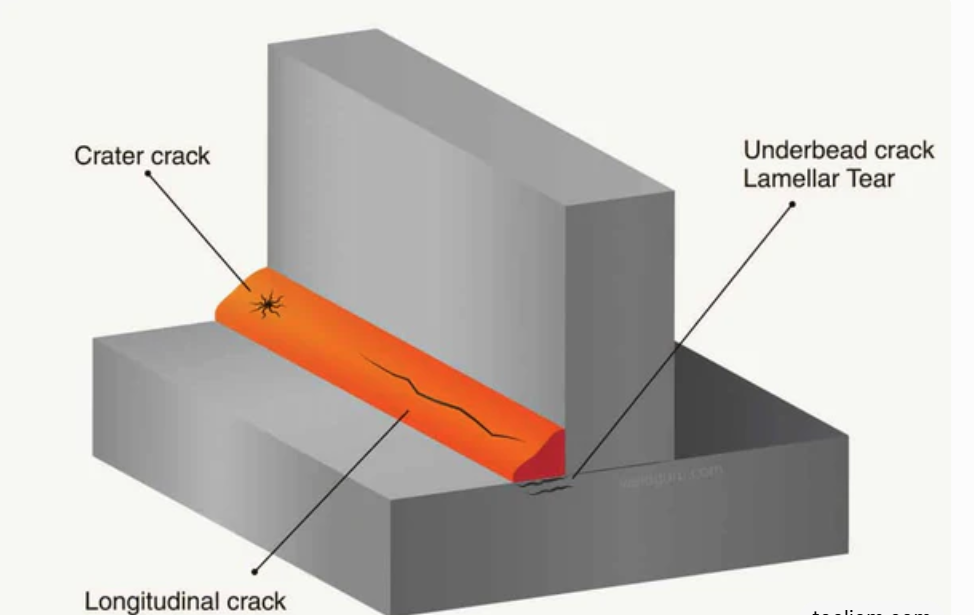
Proper preparation is crucial to avoid failures. Here's a streamlined guide:
1. Identify the Type of Cast Iron: Gray cast iron is most common and weldable; white cast iron is brittle and often not weldable. Ductile iron requires specific techniques.
2. Clean the Surface: Remove rust, paint, oil, and debris using a grinder or wire brush. For deep cleaning, use solvents or electrolysis.
3. Pre-Heat if Applicable: As mentioned, uniform heating prevents cracks.
4. Choose the Right Filler Material: Nickel rods for machinable welds; iron-based for color matching.
5. Weld in Short Beads: Apply welds in 1-2 inch segments, peening each to distribute stress.
6. Post-Weld Treatment: Slow cooling, stress-relieving, and possibly machining for a smooth finish.
Pro Tips to Avoid Common Pitfalls
- Avoid Overheating: Keep heat input minimal to prevent warping.
- Use the Right Equipment: TIG or MIG welders with appropriate settings; avoid oxy-acetylene if possible, as it can introduce more carbon.
- Test for Cracks: Dye penetrant testing post-weld ensures integrity.
- Safety First: Always wear protective gear, as cast iron welding produces fumes and intense heat.
For complex jobs, like repairing engine blocks or heavy machinery, these tips underscore the value of expertise.
Why Choose Professional Welding Services?
While some minor repairs can be tackled at home, cast iron welding often demands precision that only seasoned professionals provide. At our welding business, we use state-of-the-art equipment and certified techniques to ensure your parts are restored to like-new condition—saving you time, money, and frustration. Whether it's an industrial component or a cherished heirloom, our team handles the challenges so you don't have to.
If you're facing a cast iron repair, contact us today for a consultation. Let's turn your broken pieces into reliable assets once more!
